根據世界衛生組織(World Health Organization, WHO)的定義,如果攝取足夠分量的活微生物能夠有益宿主的健康,這活微生物便是益生菌(live microorganisms which when administered in adequate amounts confer a health benefit on the host)
人體中存在大量微生物組群(microbiota),當中大部份存活在腸道裡,其餘分佈在口腔、呼吸道、皮膚、陰道等部位。當中對健康有益的微生物就是益生菌。人體微生態平衡與健康息息相關,尤其腸道微生物的組成會直接影響腸道免疫系統,進而影響整體健康。微生態平衡講求擁有足夠數量的益菌,並抑制體內害菌,維持整體健康。

益生菌在何處找?
第一批益生菌
人體上的第一批益生菌其實不假外求,早在母親懷孕的時候,微生物已經從胎盤傳給胎兒,然後在分娩時,母親的陰道內的益生菌便傳給嬰兒,成為寶寶出生的第一份禮物,有利於寶寶健康成長。反之,剖腹產的嬰兒的腸道微生物組群跟順產的不同,她們得到過敏疾病的風險也比較高,而且腸道微生物組群的結構在大約三歲後大致成形,因此益生菌對嬰兒的健康成長非常重要。
找到益生菌的食品
益生菌在很多食品裡可以找到,尤其是奶類製品豆類製品和經過發酵的食品,例如乳酪(yoghurt)、酪漿(buttermilk)、酸菜(pickles)、泡菜(kimchi)、納豆(natto)、克菲爾(kefir)、德式酸菜(sauerkraut)、味噌(miso)、紅茶菌(kombucha)等等。
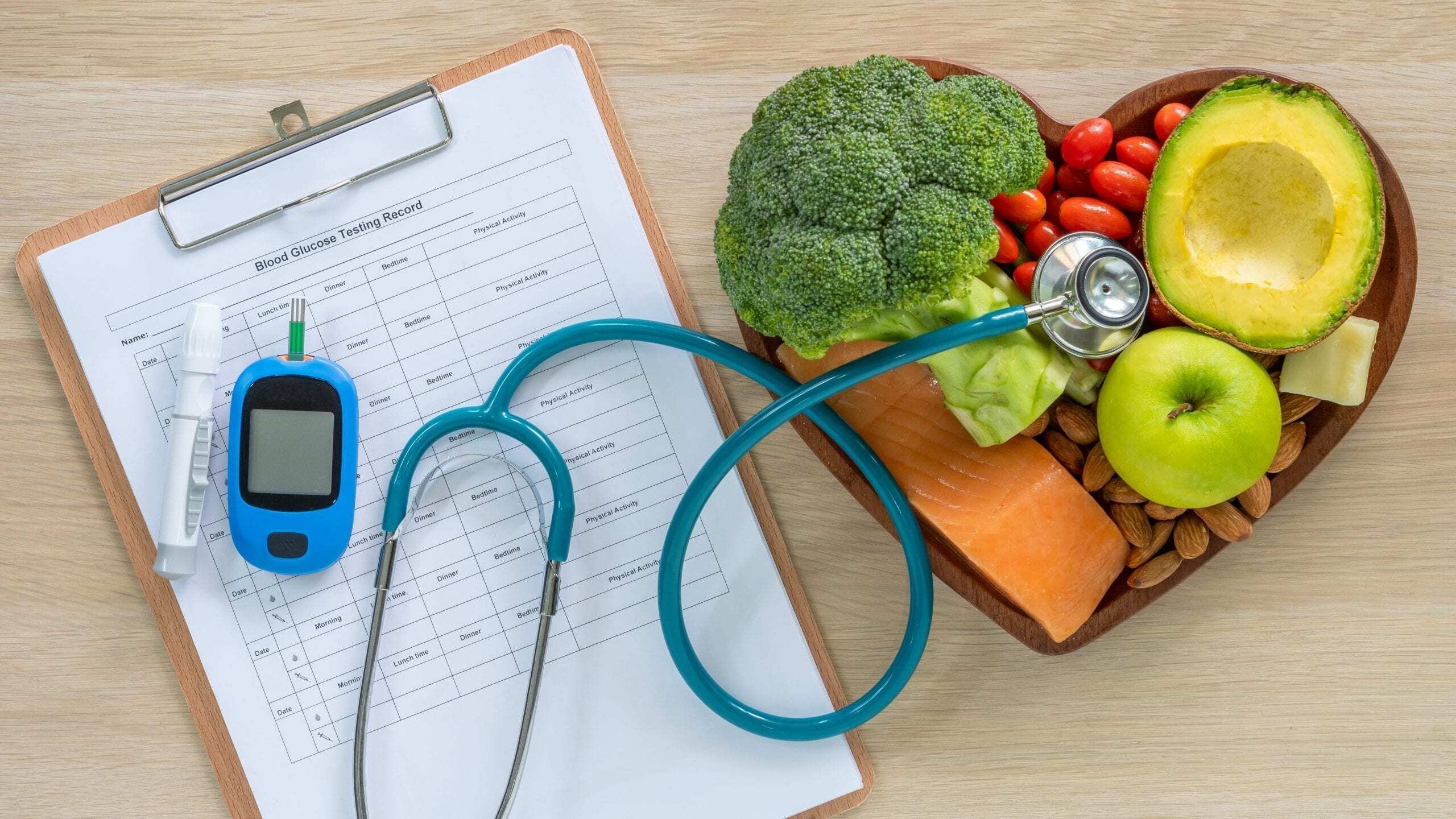
益生菌的好處
- 腸道健康
- 控制過敏
- 對抗肥胖
- 精神健康
益生菌能夠有效改善腸道環境和消化系統。益生菌能夠產生多種酶消化食物,並製造人體所需的維生素、葉酸、胺基酸等物質,並協助分解有害物,保持腸道細胞的緊密連接,阻止有害細菌和病毒入侵。
益生菌可以緩和腸胃不適和腹瀉,包括因服食抗生素或由難辨梭菌(Clostridioides difficle)感染引致的腹瀉。益生菌會製造不同抗菌物質,抵禦細菌和病毒入侵。另外,益生菌會調節腸道活動,增加蠕動,改善便秘。另外,益生菌亦有減低發炎的功能,所產生的短鏈脂肪酸(short chain fatty acids, SCFAs),可以降低發炎程度,促進腸道內微生態回復平衡。
益生菌有助調控免疫系統和對抗過敏。大量科學研究佐證益生菌可以應用於與免疫系統和過敏有關的疾病,例如食物過敏等。通過調和免疫反應機制間的平衡,例如調控輔助T細胞中(helper T cells)Th1和Th2的數量和活躍程度,調整不同細胞因數(cytokines)的含量,控制過敏反應。
肥胖和糖尿病是非常常見的慢性疾病,都是因為攝取過多能量,引致中央能量代謝失調的結果。過多糖分會使細胞超出負荷,升高血糖,又會轉化成脂肪,然後引致慢性發炎反應;過多膽固醇會形成難以溶解的斑塊(plaque),積聚在血管壁,引起慢性發炎。益生菌能夠調控腸胃激素的分泌,降低血糖,維持糖和脂肪代謝的體內平衡,並降低膽固醇積聚的風險。此外,益生菌也影響對飽餓信號的控制,達到抑制食欲的效果。
很多研究指出,腸道微生物組群會影響大腦的資訊傳遞和精神健康,例如情緒、壓力、焦慮等現象都跟腸道微生物有關,這就是腸道微生物組群調控腸道跟大腦的聯繫機制、即是腸-腦軸(gut-brain axis)。有研究發現益生菌會產生神經傳導物質(neurotransmitters),包括色胺酸(tryptophan)、γ-胺基丁酸(γ-aminobutyric acid)、血清素(serotonin)、去甲腎上腺素(noradrenaline)等等,有助減輕焦慮和憂鬱症狀,甚至改善自閉症。腸道微生物組群、益生菌、和精神健康三者的關係,已經成為生物醫學研究上一個新領域。
常見益生菌株的功效
乳雙歧桿菌
(Bifidobacterium lactis)
副乾酪乳桿菌
(Lactobacillus paracasei)
植物乳桿菌
(Lactobacillus plantarum)
嗜酸乳桿菌
(Lactobacillus acidophilus)
能夠分泌抗生素相近物質
⾧雙歧桿菌
(Bifidobacterium longum)
鼠李糖乳桿菌
(Lactobacillus rhamnosus)
為腸道黏性強,並且容易在腸道內定 植
乳雙歧桿菌
(Bifidobacterium lactis)



副乾酪乳桿菌
(Lactobacillus paracasei)




植物乳桿菌
(Lactobacillus plantarum)




益生菌?益生元?後生元?
人類和益生菌都是生物,我們以為如果益生菌死掉了,她們的功能便失去,不能發揮作用,一切到此為止,原來並不是,科學家發現死菌也有類似活菌的作用。事實上,益生菌活體的衍生物質,包括死菌、細胞碎片、和代謝產物等物質對人體都是有益的東西,統稱為後生元(postbiotics)。至於我們常聽到的益生元(prebiotics),是益生菌的食物、而宿主不能消化的物質,並對宿主的健康有益,常見的有菊糖(inulin)、半乳糖寡糖(galactooligosaccharides)和果糖寡糖(fructooligosaccharides)。很多益生菌產品,有加入益生元一併使用以增進效能,便成為合生元(synbiotics)。
後生元解構
後生元有很多種類,有從培養液提取的無細胞上清液(supernatants)、細胞發酵產物、破碎細胞後的細胞壁碎片、細胞溶解產物(cell lysates)、胞外囊泡(extracellular vesicles)等等。從化學性質來說,後生元也包括胞外多糖(exopolysaccharides)、磷壁酸(teichoic acid)、肽聚醣(peptidoglycan)、酶(enzymes)、短鏈脂肪酸(short chain fatty acids, SCFAs)、有機酸(organic acids)、細菌素(bacteriocins)、維生素(vitamins)、葉酸(folic acid)、多酚(polyphenols)等等,林林總總。其實很多人體必需的營養、例如維生素B12、維生素K、葉酸等,都是由益生菌合成供應,我們的健康真是有賴她們的貢獻。
既生瑜,何生亮?
既然益生菌那麼有益,有效又安全,為什麼需要後生元?雖然益生菌十分安全,安全劑量很高,但是對於部分長期病患、腸道屏障不健全的人來說,都需要慎用,考慮有感染和過度刺激免疫系統的風險,又不能排除得到對抗生素抗藥性的機會,因此後生元可以避免使用活菌的風險,安全性可能更勝一籌。因為後生元不是活菌,所以可以減少依賴低溫儲存,儲存比較容易,保質期可以更長,運輸也更加方便。後生元應用在健康產業的潛力,是未來的新領域。
參考資料:
Kerry RG, Patra JK, Gouda S, Park Y, Shin HS, Das G. Benefaction of probiotics for human health: a review. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis, 2018, 26(3), 927-939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2018.01.002
Sanders ME, Merenstein DJ, Reid G, Gibson GR, Rastall RA. Probiotics and prebiotics in intestinal health and disease: from biology to the clinic. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 2019, 16, 605-616. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-019-0173-3
Wang HT, Anvari S, Anagnoustou K. The role of probiotics in preventing allergic disease. Children, 2019, 6, 24. doi:10.3390/children6020024
Tillisch K. The effect of gut microbiota on CNS function in humans. Gut Microbes, 5(3), 404-410. DOI: 10.4161/gmic.29232
Sarker A, Sehto SM, Harty S, Dinan TG, Cryan JF, Burnet PWJ. Psychobiotics and the manipulation of bacteria-gut-brain signals. Trends in Neurosciences, 2016, 39(11),763-781. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2016.09.002 763
Noonan S, Zaveri M, Macaninch E, Martyn K. Food & mood: a review of supplementary prebiotic and probiotic interventions in the treatment of anxiety and depression in adults. BMJ Nutrition, Prevention & Health, 2020, 0. doi:10.1136/bmjnph-2019-000053
Moore RE, Townsend SD. Temporal development of the infant gut microbiome. Open Biology, 2019, 9, 190128. http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rsob.190128
Medical News Today. Benefits of probiotics. Accessed on 15 Decemeber 2020. Available at: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/264721
Medical News Today. Probiotic foods: what to know? Accessed on 15 Decemeber 2020. Available at: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/323314
Cleveland Clinic. Probiotics. Accessed on 15 Decemeber 2020. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/14598-probiotics
Harvard Health Publishing. Health benefits of taking probiotics. Accessed on 15 Decemeber 2020. Available at: https://www.health.harvard.edu/vitamins-and-supplements/health-benefits-of-taking-probiotics
參考文獻:
Hou YH, Lin SW, Zhao C, Lu HC, Chen YL, Lin WH, Chen CC. Effect of Bifidobacterium lactis GKK2 on OVA-induced asthmatic mice. Hans Journal of Biomedicine, 2019, 9(2), 70-80.
Hou YH, Lin SW, Wu CJ, Chen YL, Chen CC. Potential protective effect of lactic acid-producing bacteria against influenza A virus infection. Journal of Testing and Quality Assurance, 2020, 9, 148-154.
Rizzardini G, Eskesen D, Calder PC, Capetti A, Jaspersen L, Clerici M. Evaluation of the immune benefits of two probiotic strains Bifidobacteriu animalis ssp. lactis, BB-12 and Lactobacillus paracasei ssp. paracasei, L. casei 431 in an influenza vaccination model: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. British Journal of Nutrition, 2012, 107, 876-884.
Jungersen M, Wind A, Johansen E, Christensen JE, Stuer-Lauridsen B, Eskesen D. The science behind the probiotic strain Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12. Microorganisms, 2014, 2, 92-110.
參考文獻:
Hill D, Sugrue I, Tobin C, Hill C, Stanton C, Ross RP. The Lactobacillus casei group: history and health related applications. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9, 2107.
Wang CS, Lin SW, Zhao C, Chen YL, Tsai PC, Chen CC. Hypoglycemic effect of Lactobacillus paracasei GKS6. Hans Journal of Food and Nutrition Science, 2019, 8(1), 9-16.
Tsai YS, Lin SW, Chen YL, Chen CC. Effect of probiotics Lactobacillus paracasei GKS6, L. plantarum GKM3, and L. rhamnosus GKLC1 on alleviating alcohol-induced alcoholic liver disease in a mouse model. Nutrition Research and Practice, 2020, 14, e41.
Yang LC, Lin, SW, Li IC, Chen YP, Tzu SY, et al. Lactobacillus plantarum GKM3 and Lactobacillus paracasei GKS6 supplementation ameliorates bone loss in ovariectomized mice by promoting osteoblast differentiation and inhibiting osteoclast formation. Nutrients, 2020, 12, 1914. doi:10.3390/nu12071914.
Choi JH, Moon CM, Shin TS, Kim EK, McDowell A, Jo MK, Joo YH, Kim SE, Jung HK, Shim KN, Jung SA, Kim YK. Lactobacillus paracasei-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate the intestinal inflammatory response by augementing the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. Experimental & Molecular Medicine, 2020, 52, 423-437.
Benyacoub J, Bosco N, Bkanchard C, Demont A, Philippe D,Castiel-Higounenc I, Gueniche A. Immune modulation property of Lactobacillus paracasei NCC2461 (ST11) strain and impact on skin defences. Beneficial Microbes, 2014, 5(2), 129-136.
參考文獻:
Lin SW, Shu JR, Chang WT, Wang CS, Zhao C, et al. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum GKM3 on obesity in high-fat diet-induced rats. Hans Journal of Food and Nutrition Science, 2017, 6(2), 85-95. https://doi.org/10.12677/hjfns.2017.62009
Hsu CL, Hou YH, Wang CS, Lin SW, Jhou BY, et al. Antiobesity and uric acid-lowering effect of Lactobacillus plantarum GKM3 in high-fat-diet-induced obese rats. Journal of American College of Nutrition, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2019.1571454
Tsai YS, Lin SW, Chen YL, Chen CC. Effect of probiotics Lactobacillus paracasei GKS6, L. plantarum GKM3, and L. rhamnosus GKLC1 on alleviating alcohol-induced alcoholic liver disease in a mouse model. Nutrition Research and Practice, 2020, 14, e41.
Yang LC, Lin, SW, Li IC, Chen YP, Tzu SY, et al. Lactobacillus plantarum GKM3 and Lactobacillus paracasei GKS6 supplementation ameliorates bone loss in ovariectomized mice by promoting osteoblast differentiation and inhibiting osteoclast formation. Nutrients, 2020, 12, 1914. doi:10.3390/nu12071914.
Prakoewska CRS, Bonita L, Karim A, Herwanto N, Umborowati MA, et al. Beneficial effect of Lactobacillus plantarum IS-10506 supplementation in adults with atopic dermatitis: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Dermatological Treatment, 2020 Nov 8, 1-8. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2020.1836310.
