
- 「青春雙歧桿菌」經本地大學科研證實,有效提高新冠疫苗成效
- 專利益菌 GKM3 配方平衡腸道益菌,增強抵禦力
- 四重雙歧桿菌有助促進抗體產生,減少「長新冠」症狀風險
- 每包含200億專業益生菌,有齊您每天所需的維生好菌
- 10種高效抗胃酸益生菌直達腸道
- 益菌精華後生元HK-LP ,迅速平衡腸道微生態,舒緩腸道不適
- 三重滋潤好菌益生元,加強益生菌定殖,幫助腸道排走毒素
- 國際標準 GMP/ISO22000 生産,安全可靠
- Passed the heavy metal test
- 無添加香料、乳蛋白製品或麩質
HK$440
Suitable for
呼吸道易敏不適

經常有口氣或口腔問題

免疫力不足,經常疲倦乏力

病後引致的腸道不適
Product Characteristics
腸道細菌的好壞直接影響身體的免疫力、新陳代謝及排毒功能等。補充益生好菌有助提升免疫屏障,恢復精神活力。
新冠肺炎疫情爆發後,很多人腸道不適的情況增加,被稱爲「新冠腸胃」。腸胃不適成因可能與腸道壞菌過度生長有關。其不適表現包括腹痛、排便習慣改變、作嘔、消化不良、飽脹感和胃食道逆流等。近期報告指出嗜酸乳桿菌對新冠病人預防抗生素相關性腹瀉 (AAD)起了強大的作用[1]。雙歧桿菌如長雙歧桿菌對「長新冠」症狀有減輕和預防的效果,特別是腸胃不適如腹痛 、腹瀉和作嘔[2]。
本地大學研究指出8成半的香港人缺少青春雙歧桿菌。另外臨床研究發現青春雙歧桿菌能調控接種疫苗後的抗體反應,在調控新冠疫苗的成效上擔當關鍵角色[3]。亦有研究數據顯示新冠肺炎患者缺乏幾種雙歧桿菌菌種,與新冠肺炎病情嚴重程度有關[4]。VitaBac Immune Pro中的四重雙歧桿菌配方有助增強身體抵禦力,當中包括雙叉雙歧桿菌能增加白血球介素的數量[5],有助調節免疫系統,提升自身免疫力。長雙歧桿菌還有助調節靜息神經活動和改善精神疲勞情況[6]。
現代都市人大多呼吸道易敏不適除了因為外在致敏物質變多外,也可能是腸道微生態失衡,導致免疫調控機制出問題,例如Th2細胞過分活躍就會容易引致過敏疾病,如不停打噴嚏,同時氣管會容易受致敏原影響。PGut VitaBac Immune Pro 含有鼠李糖乳桿菌有助減輕上呼吸道症狀和發病率[7]。產品中還含有副乾酪乳桿菌可以調節免疫反應,減低免疫細胞過分活躍的情況[8]及上呼吸道敏感的發病時間[9]。
口氣大多來自口腔細菌分解食物殘渣的蛋白質時產生揮發性硫化物的臭味。另外煙酒習慣、口腔及腸道疾病、藥物療程等都有機會造成口臭。研究指出洛德乳桿菌有助減低牙齦炎和蛀牙患者牙齦溝液中的促炎細胞因子,減少發炎引致的口臭問題[10]。此外,洛德乳桿菌產生的細菌素和副乾酪乳桿菌可以抑制口腔壞菌繁殖,有助改善蛀牙及牙周病的情況[11]。
從加熱滅活的植物乳桿菌抽取的精華就是後生元,性質穩定。研究顯示後生元植物乳桿菌能改善免疫力功能,抑制過分活躍的免疫細胞和過敏的抗體,也有助於調節腸道菌群的組成,促進有益細菌的生長,平衡腸道微生態。
Product Highlight
10X加強版 青春雙歧桿菌 有效提高新冠疫苗成效,增強保護力
四重雙歧桿菌配方 有助促進抗體產生,減少「長新冠」症狀風險
Suitable for vegetarians and people with general eating habits.
一包有齊您每天所需的維生好菌

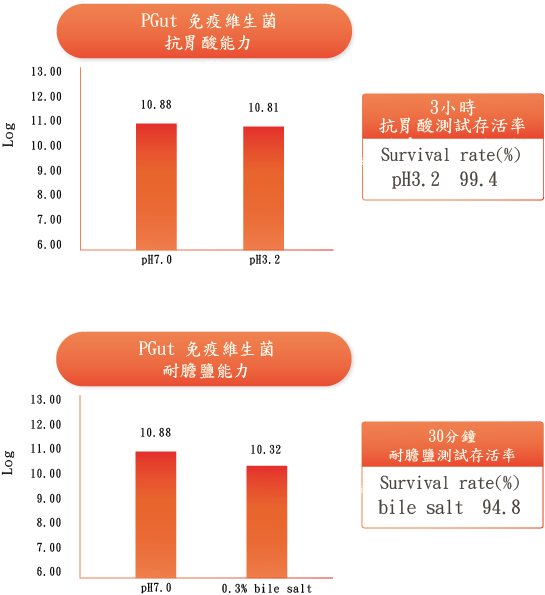
PGut 免疫維生菌 passes the acidic and bile salt resistance test:
Important Messages
Contents
✔︎ 30包/盒 (每包含200億活性益生菌)
✔︎ 10 active probiotics + 3 prebiotics + postbioticsUsage
✦ Instruction of use: Consume together with food and drink (E.g. milk and juice)
✦ 建議用量﹕每日一包,飯前飯後食用均可
Other information
- Origin: Taiwan
- Store in fridge or in a cool and dry area. Avoid sunlight.
- Please inform your doctor if you are pregnant, taking medicine or any treatment.
Reference
- Kullar, R., Johnson, S., McFarland, L. V., & Goldstein, E. J. (2021). Potential roles for probiotics in the treatment of COVID-19 patients and prevention of complications associated with increased antibiotic use. Antibiotics, 10(4), 408.
- Mirashrafi, S., Moravejolahkami, A. R., Zehi, Z. B., Kermani, M. A. H., Bahreini-Esfahani, N., Haratian, M., … & Pourhossein, M. (2021). The efficacy of probiotics on virus titres and antibody production in virus diseases: A systematic review on recent evidence for COVID-19 treatment. Clinical Nutrition ESPEN, 46, 1-8.
- Ng, S. C., Peng, Y., Zhang, L., Mok, C. K., Zhao, S., Li, A., … & Tun, H. M. (2022). Gut microbiota composition is associated with SARS-CoV-2 vaccine immunogenicity and adverse events. Gut, 71(6), 1106-1116.
- Hazan, S., Stollman, N., Bozkurt, H. S., Dave, S., Papoutsis, A. J., Daniels, J., … & Borody, T. J. (2022). Lost microbes of COVID-19: Bifidobacterium, Faecalibacterium depletion and decreased microbiome diversity associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection severity. BMJ open gastroenterology, 9(1), e000871.
- Hong, N., Ku, S., Yuk, K., Johnston, T. V., Ji, G. E., & Park, M. S. (2021). Production of biologically active human interleukin-10 by Bifidobacterium bifidum BGN4. Microbial Cell Factories, 20(1), 1-14.
- Wang H, Braun C, Murphy EF, Enck P: Bifidobacterium longum 1714™ strain modulates brain activity of healthy volunteers during social stress. The American journal of gastroenterology 2019, 114(7):1152.
- Kumpu, M., Kekkonen, R. A., Korpela, R., Tynkkynen, S., Järvenpää, S., Kautiainen, H., … & Winther, B. (2015). Effect of live and inactivated Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG on experimentally induced rhinovirus colds: randomised, double blind, placebo-controlled pilot trial. Beneficial microbes, 6(5), 631-639.
- Benyacoub J, Bosco N, Blanchard C, Demont A, Philippe D, Castiel-Higounenc I, Guéniche A: Immune modulation property of Lactobacillus paracasei NCC2461 (ST11) strain and impact on skin defences. Beneficial microbes 2014, 5(2):129-136.
- Jespersen, L., Tarnow, I., Eskesen, D., Morberg, C. M., Michelsen, B., Bügel, S., … & Calder, P. C. (2015). Effect of Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei, L. casei 431 on immune response to influenza vaccination and upper respiratory tract infections in healthy adult volunteers: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study. The American journal of clinical nutrition, 101(6), 1188-1196.
- Karbalaei, M., Keikha, M., Kobyliak, N. M., Zadeh, Z. K., Yousefi, B., & Eslami, M. (2021). Alleviation of halitosis by use of probiotics and their protective mechanisms in the oral cavity. New Microbes and New Infections, 42, 100887.
- Bonifait, L., Chandad, F., & Grenier, D. (2009). Probiotics for oral health: myth or reality?. Journal of the Canadian Dental Association, 75(8).
Reference Test Laboratory: Biotech Research Institute, No.402, Sec. 2, Jinling Rd., Pingzhen Dist., Taoyuan City 324, Taiwan (R.O.C.)
Disclaimer: For details, please refer to the label on the product. The picture above is for reference only. The real object should be considered as final. This product is not registered under the Pharmacy and Poisons Ordinance or the Chinese Medicine Ordinance. Any claim made for it has not been subject to evaluation for such registration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat or prevent any disease.
